Understanding Vertical Jump
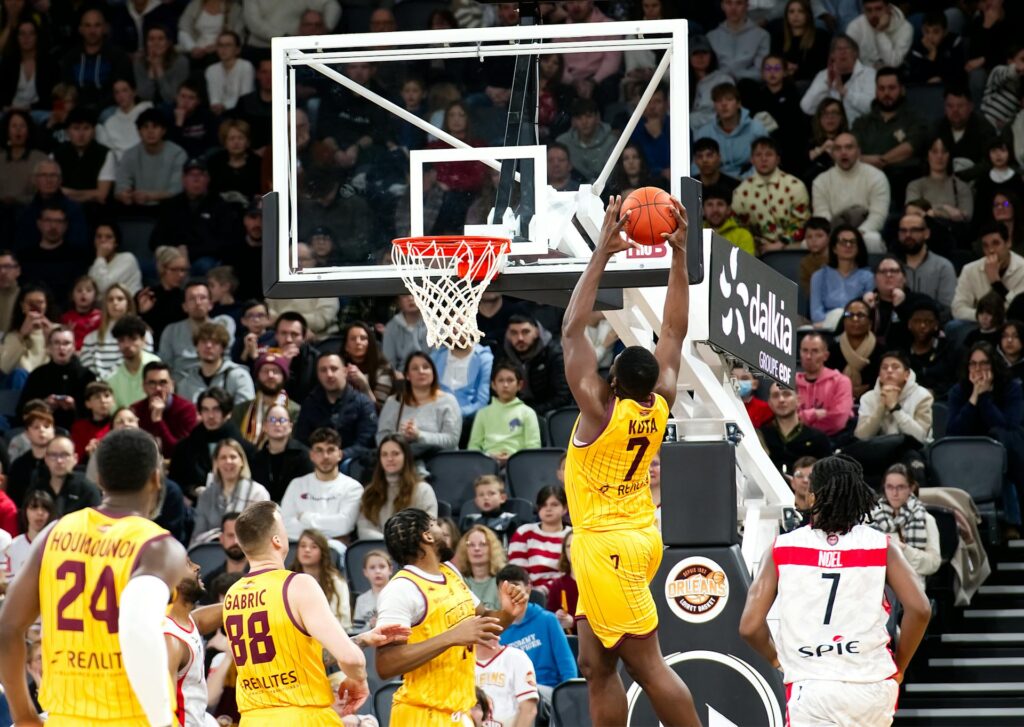
The vertical jump is a crucial athletic skill for basketball players that reflects their ability to elevate off the ground. It is defined as the distance a player can leap vertically from a standing position or with a running start. The significance of vertical jump in basketball cannot be overstated, as it directly correlates with a player’s performance on the court. A higher vertical leap enhances a player’s scoring ability, defensive capabilities, and rebounding performance, enabling them to reach for the hoop or challenge opponents more effectively.
Biomechanically, the vertical jump involves a complex interaction between the muscles, tendons, and neuromuscular system. The jump starts with a preparatory phase known as the counter-movement, where the player bends their knees and lowers their center of mass. This action is followed by an explosive upward movement, where the force generated through the legs propels the body upwards. The efficiency of this motion relies deeply on the strength of the lower body musculature, as well as proper technique, which includes arm usage and body positioning. As players leverage their core and leg strength, they achieve higher verticals, which significantly contributes to their overall game performance.
When examining vertical jump statistics, it is important to understand the averages for various levels of basketball players. High school players typically have an average vertical jump around 20 inches, while collegiate athletes may average closer to 28-30 inches. Elite basketball players, especially those on professional teams, often boast vertical jumps exceeding 35 inches. Understanding these benchmarks helps aspiring athletes set realistic goals for enhancing their own vertical leap, thereby improving their on-court effectiveness and competitiveness.
Assessing Your Current Vertical Jump
Understanding your current vertical jump is an essential first step in enhancing your performance in basketball. Accurately measuring your vertical jump not only provides a benchmark for improvement but also helps in setting achievable goals. There are several methods available for assessing your vertical leap, each with its own advantages.
One of the simplest techniques to measure your vertical jump involves the use of a measuring tape. Begin by marking the maximum height you can reach while standing flat-footed with one hand raised. Next, jump as high as you can and mark the highest point you reach during the jump. The difference in height between the two marks represents your vertical jump. Although this method is straightforward, it can be improved with additional tools for more precise measurements.
An increasingly popular method for measuring vertical jumps is the use of a jump mat. These mats are designed to accurately record the height of your jump by detecting the moment you leave the ground and when you land, providing a more reliable reading. This technique is beneficial for athletes who seek consistent results and immediate feedback on their performance.
There are also various vertical jump trainers available on the market, which not only measure your jump but can also assist in training exercises tailored to improve your vertical leap. These devices often provide training programs to enhance muscle strength and explosive power, key factors in boosting your jump height.
Regardless of the method you choose, it is crucial to track your progress consistently. Documenting your vertical jump measurements over time allows you to set realistic goals and witness improvements in your performance, fostering motivation and engagement in your training process. Evaluate your current vertical jump regularly to make informed decisions regarding your training regimen.
Strength Training for Jump Improvement
Enhancing vertical jump ability is a multifaceted endeavor, and strength training plays a pivotal role in this process. By focusing on exercises that strengthen key muscle groups—namely the legs, core, and lower back—athletes can significantly improve their jumping capabilities. The foundation of a powerful jump lies in muscular strength and explosive force, making targeted strength training essential.
One of the most effective exercises for increasing vertical jump is the squat. Squats engage multiple muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. This comprehensive engagement not only contributes to overall leg strength but also promotes the development of muscle coordination, which is crucial for executing powerful jumps. Variations such as front squats and jump squats can further enhance explosiveness due to their dynamic nature.
Deadlifts are another cornerstone of strength training for jump improvement. By targeting the posterior chain—the muscles along the back of the body, including the hamstrings and glutes—deadlifts facilitate the generation of power necessary for vertical jumps. Moreover, this exercise helps improve stability and posture, further aiding in jump performance.
Plyometric exercises are especially beneficial for developing explosive strength essential for vertical jumping. Movements such as box jumps, depth jumps, and bounding utilize the stretch-shortening cycle of the muscles, enhancing the fast-twitch muscle fibers that contribute to explosive jumping motion. Incorporating these exercises into a regular training routine can significantly boost jump height and overall athletic performance.
Creating a balanced workout plan that includes these exercises, along with sufficient rest and recovery, ensures optimal strength gains and jump improvement. By integrating strength training into your regimen, you will be well on your way to achieving greater vertical leap heights on the basketball court.
Plyometric Exercises to Boost Vertical Leap
Plyometric training plays a vital role in enhancing vertical jump performance, particularly for basketball players. It comprises explosive movements that improve muscle power and agility, which are essential for reaching greater heights during jumps. By incorporating specific plyometric exercises into a disciplined training regimen, athletes can significantly boost their vertical leap.
Among the most effective plyometric exercises, box jumps stand out for their ability to develop explosive power. This exercise involves jumping onto a stable box or platform, emphasizing a strong upward thrust. The practice not only strengthens the lower body but also enhances the coordination between muscles and the nervous system. To maximize the efficacy of box jumps, it is recommended to perform them for about three sets, with each set consisting of 8 to 10 repetitions.
Depth jumps are another highly beneficial plyometric exercise that aids in vertical jump improvement. The movement requires the athlete to step off a box and immediately jump upon landing. This action harnesses the stretch reflex of the muscles, thus training the body to react explosively. Like box jumps, depth jumps should be incorporated into workouts with caution, focusing on quality over quantity to prevent injury. Performing around three to five sets of 5 to 8 jumps can yield significant gains.
Jump squats serve as an excellent addition to a plyometric routine as well. They incorporate the mechanics of squatting and jumping, targeting muscles necessary for powerful jumps. To execute a jump squat, start in a squat position and explode upward, landing softly back into the squat. Consistency in practicing this exercise, around three sets of 10 to 15 reps, can enhance both strength and explosive power, contributing positively to vertical leap progression.
Incorporating these plyometric exercises into a regular training program can yield impressive improvements in vertical jump for basketball players. The key is to maintain proper form and gradually increase intensity over time, allowing for optimal gains while minimizing the risk of injury.
Speed and Agility Drills
Increasing your vertical jump for basketball is not solely dependent on strength training; speed and agility also play a crucial role in enhancing your overall performance on the court. The ability to move quickly and change directions efficiently can significantly contribute to your jumping ability. To facilitate this improvement, incorporating a variety of speed and agility drills into your training regimen is essential.
One effective drill is the ladder drill, which focuses on footwork and body coordination. By performing a series of quick steps through an agility ladder, players can develop their speed and sharpen their motor skills. This drill not only helps improve foot speed but also enhances the nerve signaling involved in quick movements, contributing to more explosive jumps.
Another valuable exercise is the cone drill, which emphasizes both speed and agility during lateral movements. Setting up cones in a zigzag pattern allows athletes to practice sprinting and cutting at varying angles. This drill encourages proper jump mechanics as players learn to explode off their outside foot, which is vital for maximizing vertical leap.
Sprints are also a fundamental component of improving athleticism. Performing short sprints (20-40 yards) can elevate your heart rate and improve your fast-twitch muscle fibers. These fibers are essential for explosive actions, such as jumping. As you become more proficient in sprints, you may find your ability to accelerate during a jump increases as well.
Incorporating these speed and agility drills into your training not only enhances your vertical jump but also contributes to better overall basketball performance. Improving your quickness can lead to more effective jumping and ensure that you can execute your plays with precision and athleticism. Prioritizing these drills will ultimately facilitate your journey to becoming a better basketball player.
Flexibility and Mobility Training
Enhancing vertical jump capabilities in basketball players requires not only strength but also optimal flexibility and mobility. Flexibility refers to the ability of muscles and joints to move through a full range of motion, while mobility encompasses the strength required to control that full range of motion. Inadequate flexibility can lead to limitations in movement patterns, potentially hindering an athlete’s jumping performance.
Focusing on specific muscle groups is crucial for improving mobility. The hip flexors, hamstrings, and calves are essential in jumping mechanics; therefore, incorporating targeted exercises for these muscles can yield significant benefits. For instance, stretches such as the hip flexor stretch and the standing hamstring stretch can help alleviate tension and improve flexibility in the hip region. This increased range of motion allows for better mechanics during jumps, leading to higher elevation.
Furthermore, calf flexibility plays an important role in vertical jump training. Exercises like calf raises and seated calf stretches can enhance calf muscle elasticity, allowing for more effective propulsion during jumping movements. These exercises can be easily integrated into a regular training routine, providing substantial benefits.
A proper warm-up routine is paramount to prepare the body for intense physical activities. Dynamic stretches that mimic jumping motions, such as leg swings and lunges, increase blood flow to the target muscle groups, enhancing mobility and reducing the risk of injuries. Conversely, a comprehensive cooldown routine helps in muscle recovery and maintains flexibility over time by preventing stiffness.
Ultimately, improved flexibility and mobility not only facilitate a greater vertical jump but also contribute to overall athletic performance. By adhering to a consistent training regimen that emphasizes these components, athletes can maximize their jumping abilities while minimizing the risk of injuries.
Nutrition’s Role in Jumping Higher
Proper nutrition plays a pivotal role in enhancing athletic performance, particularly when it comes to maximizing one’s vertical jump in basketball. A balanced diet supplies the essential nutrients required for muscle recovery, growth, and optimal energy levels. Athletes aiming to improve their vertical leap should focus on consuming a blend of macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which collectively contribute to muscle recovery and energy production.
Carbohydrates serve as the primary energy source for high-intensity activities such as jumping. Foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are critical as they provide the necessary glucose to fuel workouts and aid in recovery. Including complex carbohydrates in meals and snacks ensures sustained energy levels throughout training sessions, allowing athletes to perform effectively.
Protein is another crucial component that supports muscle repair and growth. Consuming quality protein sources such as lean meats, eggs, dairy, and plant-based alternatives can help athletes recover more quickly from strenuous workouts. This is invaluable for those training to increase their vertical jump, as repair and growth of muscle fibers are essential for improvement.
Adequate hydration cannot be overlooked in the context of nutrition. Dehydration can lead to decreased performance levels, negatively impacting an athlete’s ability to jump. Maintaining proper fluid intake before, during, and after training is essential to support optimal physical function.
Furthermore, certain vitamins and minerals can enhance athletic performance. For instance, calcium and vitamin D are vital for bone health, which is critical for jumping. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, also play a role in reducing inflammation, supporting recovery after intense workouts. Incorporating a variety of these nutrient-rich foods fosters an environment that promotes muscle adaptation and ultimately enhances vertical jump capabilities.
Recovery and Rest for Optimal Performance
Enhancing vertical jump performance in basketball requires not only dedicated training but also strategic recovery and rest periods. Recovery is a vital component of any training regimen as it allows the body to heal, adapt, and become stronger. The incorporation of rest days is essential, as these intervals give muscles the opportunity to recover from the stress of high-intensity workouts, preventing fatigue and decreasing the risk of injury.
Quality sleep plays a pivotal role in the recovery process. During sleep, the body undergoes several repair processes, including muscle recovery and hormonal regulation. Athletes should aim for a minimum of 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night for optimal performance and vertical jump enhancement. Establishing a consistent sleep routine can greatly affect energy levels and overall workout effectiveness.
In addition to rest days and sufficient sleep, recovery techniques such as foam rolling and active recovery sessions can significantly aid in improving jump performance. Foam rolling helps alleviate muscle tightness, improve blood circulation, and reduce soreness, all of which contribute to better athletic output. Active recovery, which involves performing low-intensity exercises, can also promote recovery by increasing blood flow to the muscles without overexerting them.
Listening to one’s body is key to avoiding overtraining—a state where an athlete pushes beyond physical limits, leading to both mental fatigue and potential injury. Signs of overtraining include prolonged soreness, fatigue, decreased performance, and changes in mood. By paying attention to these signals, athletes can modify their training and rest strategy accordingly, ensuring sustained progress in their vertical jump.
In conclusion, a well-rounded approach that includes recovery strategies, proper rest, and attention to bodily signals will optimize athletic performance and vertical jump capabilities in basketball. Prioritizing recovery is not merely a break from training but an integral part of an athlete’s overall success.
Tracking Progress and Adapting Your Program
To effectively increase your vertical jump for basketball, it is essential to track your progress consistently. Keeping a training log provides valuable insights into your performance and helps in identifying areas for improvement. Start by recording each workout session, making detailed notes about the exercises performed, sets, repetitions, and the intensity of each effort. Additionally, track your vertical jump measurements over time, ideally using a vertical jump tester or a simple measuring tape and a wall. This structured documentation will allow you to observe trends and adjust your training regimen accordingly.
The frequency of re-assessing your vertical jump is crucial for monitoring progress. It is advisable to evaluate your jump height at regular intervals, such as every four to six weeks. This timeline provides ample time to implement your training program while allowing for meaningful improvements to be noted. After conducting these assessments, compare your latest jump height with earlier results, and analyze any patterns. Did you experience significant gains, or did your performance plateau? Understanding the data collected will influence your next steps in training.
It’s vital to adapt your workout program based on individual performance. Identifying when to modify your training can lead to more effective results. For instance, if improvements are slow or if you’re feeling fatigued, consider incorporating additional rest days or varying the exercises to engage different muscle groups. On the other hand, if you are consistently achieving your target jump height, it may be time to increase the intensity or complexity of your workouts. These adjustments will ensure that your training remains challenging yet manageable, ultimately enhancing your vertical leap and overall athletic performance.